Audio descriptions involve narrating contextual visual information in images or videos, improving user experiences, especially for those who rely on audio cues.
At the core of audio description technology are two crucial components: the description and the audio. The description involves understanding and interpreting the visual content of an image or video, which includes details such as actions, settings, expressions, and any other relevant visual information. Meanwhile, the audio component converts these descriptions into spoken words that are clear, coherent, and natural-sounding.
So, here’s something we can do: build an app that generates and announces audio descriptions. The app can integrate a pre-trained vision-language model to analyze image inputs, extract relevant information, and generate accurate descriptions. These descriptions are then converted into speech using text-to-speech technology, providing a seamless and engaging audio experience.
By the end of this tutorial, you will gain a solid grasp of the components that are used to build audio description tools. We’ll spend time discussing what VLM and TTS models are, as well as many examples of them and tooling for integrating them into your work.
When we finish, you will be ready to follow along with a second tutorial in which we level up and build a chatbot assistant that you can interact with to get more insights about your images or videos.
Vision-Language Models: An Introduction
VLMs are a form of artificial intelligence that can understand and learn from visuals and linguistic modalities.
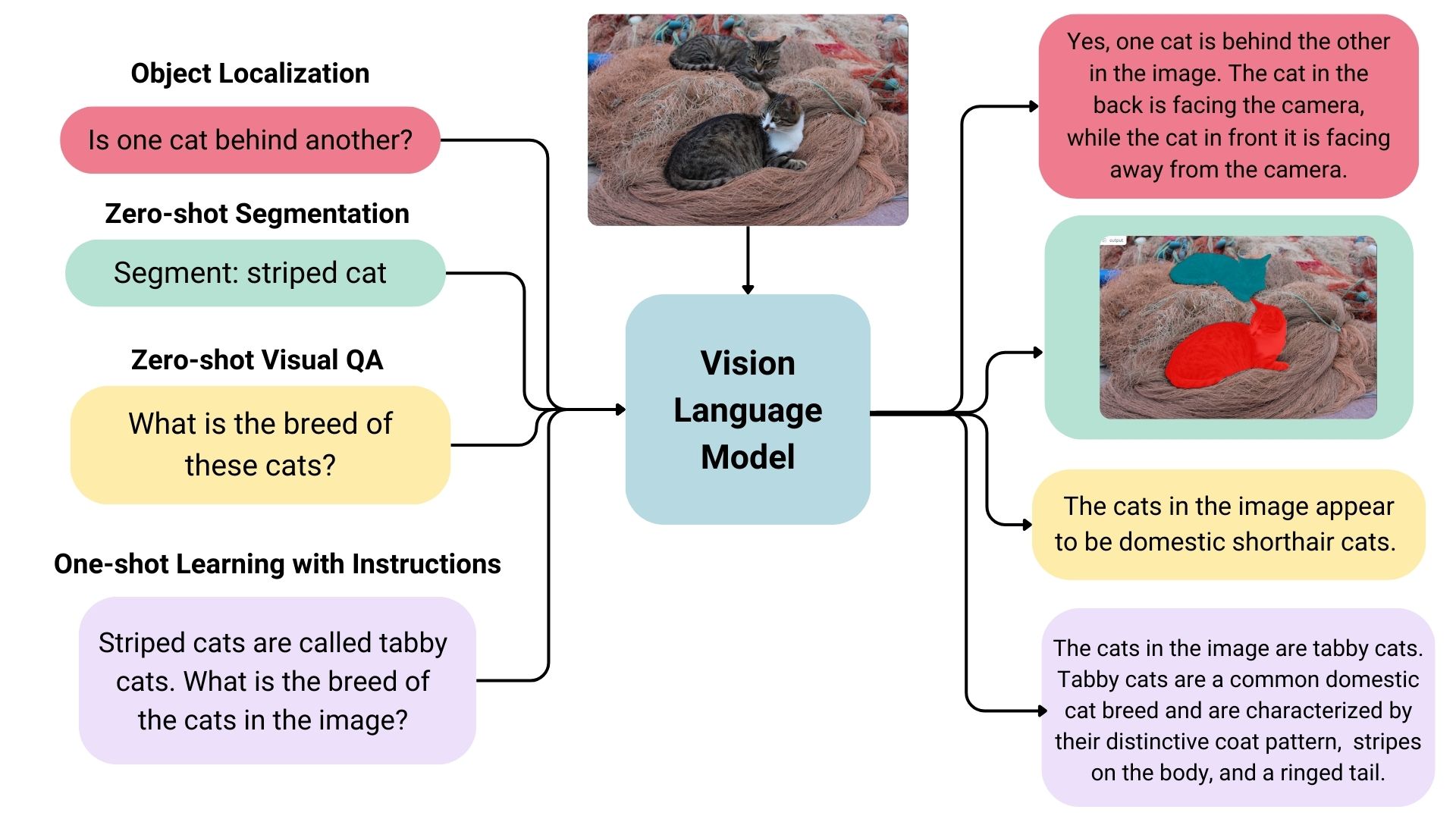
They are trained on vast amounts of data that include images, videos, and text, allowing them to learn patterns and relationships between these modalities. In simple terms, a VLM can look at an image or video and generate a corresponding text description that accurately matches the visual content.
VLMs typically consist of three main components:
- An image model that extracts meaningful visual information,
- A text model that processes and understands natural language,
- A fusion mechanism that combines the representations learned by the image and text models, enabling cross-modal interactions.
Generally speaking, the image model — also known as the vision encoder — extracts visual features from input images and maps them to the language model’s input space, creating visual tokens. The text model then processes and understands natural language by generating text embeddings. Lastly, these visual and textual representations are combined through the fusion mechanism, allowing the model to integrate visual and textual information.
VLMs bring a new level of intelligence to applications by bridging visual and linguistic understanding. Here are some of the applications where VLMs shine:
-
Image captions: VLMs can provide automatic descriptions that enrich user experiences, improve searchability, and even enhance visuals for vision impairments.
-
Visual answers to questions: VLMs could be integrated into educational tools to help students learn more deeply by allowing them to ask questions about visuals they encounter in learning materials, such as complex diagrams and illustrations.
-
Document analysis: VLMs can streamline document review processes, identifying critical information in contracts, reports, or patents much faster than reviewing them manually.
-
Image search: VLMs could open up the ability to perform reverse image searches. For example, an e-commerce site might allow users to upload image files that are processed to identify similar products that are available for purchase.
-
Content moderation: Social media platforms could benefit from VLMs by identifying and removing harmful or sensitive content automatically before publishing it.
-
Robotics: In industrial settings, robots equipped with VLMs can perform quality control tasks by understanding visual cues and describing defects accurately.
This is merely an overview of what VLMs are and the pieces that come together to generate audio descriptions. To get a clearer idea of how VLMs work, let’s look at a few real-world examples that leverage VLM processes.
VLM Examples
Based on the use cases we covered alone, you can probably imagine that VLMs come in many forms, each with its unique strengths and applications. In this section, we will look at a few examples of VLMs that can be used for a variety of different purposes.
IDEFICS
IDEFICS is an open-access model inspired by Deepmind’s Flamingo, designed to understand and generate text from images and text inputs. It’s similar to OpenAI’s GPT-4 model in its multimodal capabilities but is built entirely from publicly available data and models.
IDEFICS is trained on public data and models — like LLama V1 and Open Clip — and comes in two versions: the base and instructed versions, each available in 9 billion and 80 billion parameter sizes.
The model combines two pre-trained unimodal models (for vision and language) with newly added Transformer blocks that allow it to bridge the gap between understanding images and text. It’s trained on a mix of image-text pairs and multimodal web documents, enabling it to handle a wide range of visual and linguistic tasks. As a result, IDEFICS can answer questions about images, provide detailed descriptions of visual content, generate stories based on a series of images, and function as a pure language model when no visual input is provided.
PaliGemma
PaliGemma is an advanced VLM that draws inspiration from PaLI-3 and leverages open-source components like the SigLIP vision model and the Gemma language model.
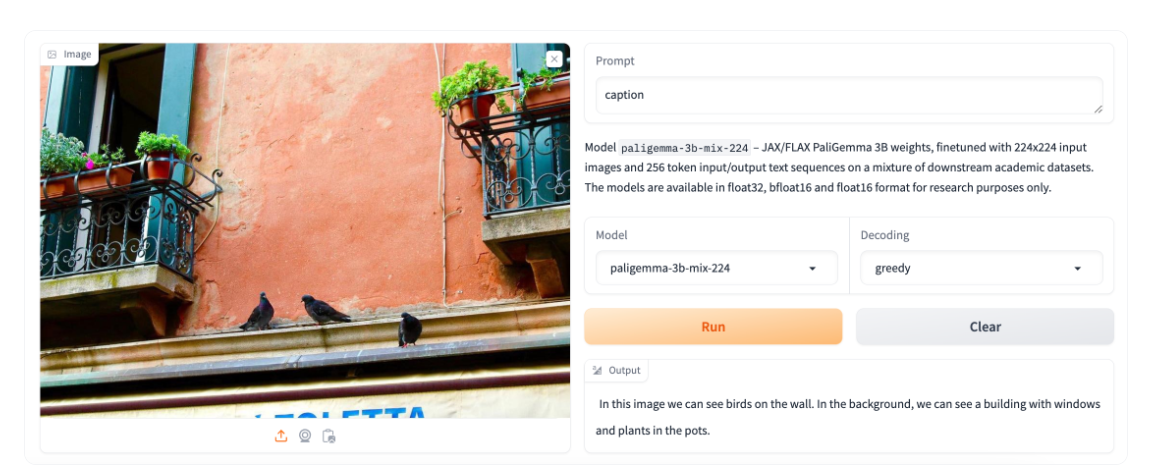
Designed to process both images and textual input, PaliGemma excels at generating descriptive text in multiple languages. Its capabilities extend to a variety of tasks, including image captioning, answering questions from visuals, reading text, detecting subjects in images, and segmenting objects displayed in images.
The core architecture of PaliGemma includes a Transformer decoder paired with a Vision Transformer image encoder that boasts an impressive 3 billion parameters. The text decoder is derived from Gemma-2B, while the image encoder is based on SigLIP-So400m/14.
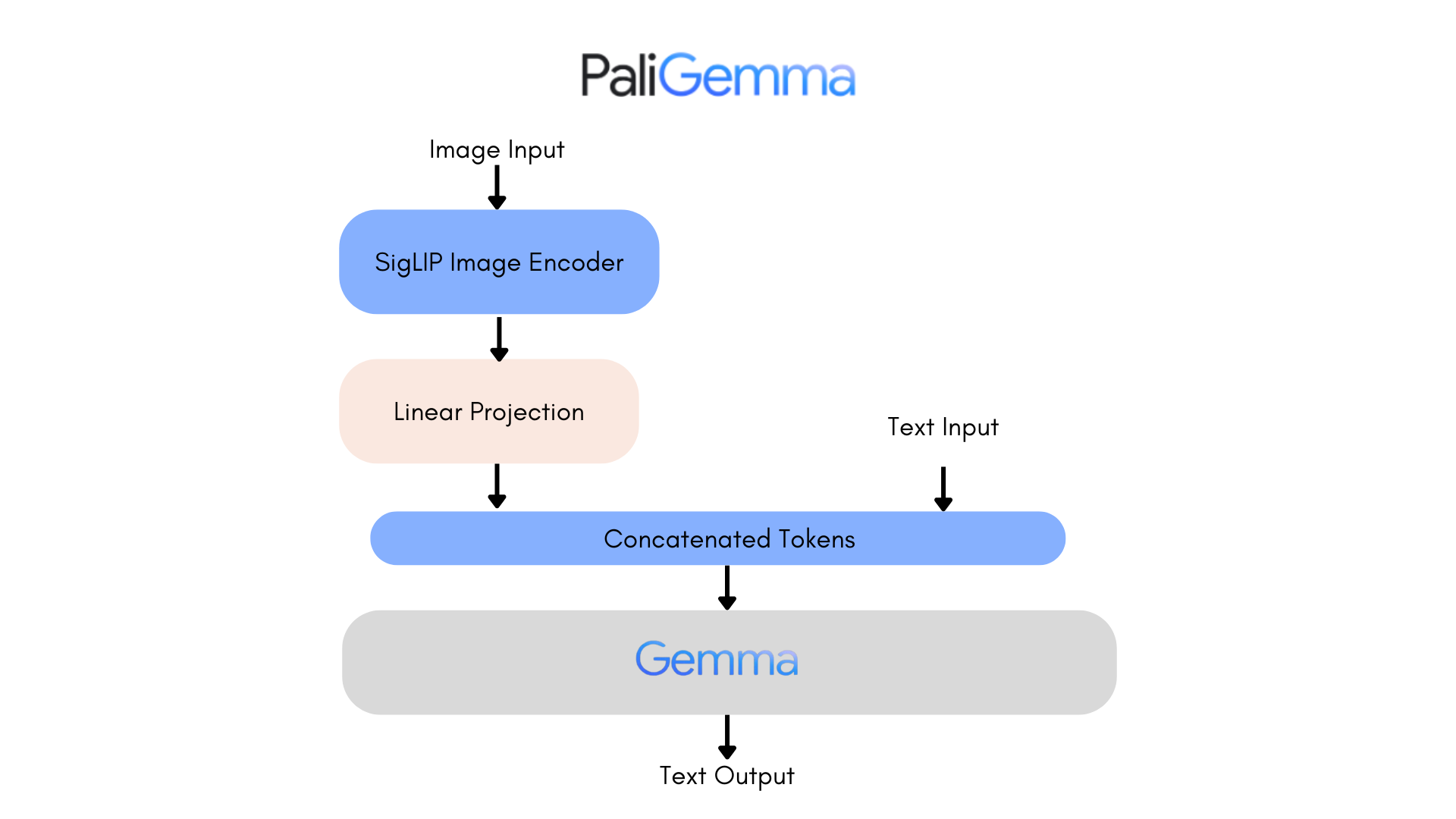
Through training methods similar to PaLI-3, PaliGemma achieves exceptional performance across numerous vision-language challenges.
PaliGemma is offered in two distinct sets:
-
General Purpose Models (PaliGemma): These pre-trained models are designed for fine-tuning a wide array of tasks, making them ideal for practical applications.
-
Research-Oriented Models (PaliGemma-FT): Fine-tuned on specific research datasets, these models are tailored for deep research on a range of topics.
Phi-3-Vision-128K-Instruct
The Phi-3-Vision-128K-Instruct model is a Microsoft-backed venture that combines text and vision capabilities. It’s built on a dataset of high-quality, reasoning-dense data from both text and visual sources. Part of the Phi-3 family, the model has a context length of 128K, making it suitable for a range of applications.
You might decide to use Phi-3-Vision-128K-Instruct in cases where your application has limited memory and computing power, thanks to its relatively lightweight that helps with latency. The model works best for generally understanding images, recognizing characters in text, and describing charts and tables.
Yi Vision Language (Yi-VL)
Yi-VL is an open-source AI model developed by 01-ai that can have multi-round conversations with images by reading text from images and translating it. This model is part of the Yi LLM series and has two versions: 6B and 34B.
What distinguishes Yi-VL from other models is its ability to carry a conversation, whereas other models are typically limited to a single text input. Plus, it’s bilingual making it more versatile in a variety of language contexts.
Finding And Evaluating VLMs
There are many, many VLMs and we only looked at a few of the most notable offerings. As you commence work on an application with image-to-text capabilities, you may find yourself wondering where to look for VLM options and how to compare them.
There are two resources in the Hugging Face community you might consider using to help you find and compare VLMs. I use these regularly and find them incredibly useful in my work.
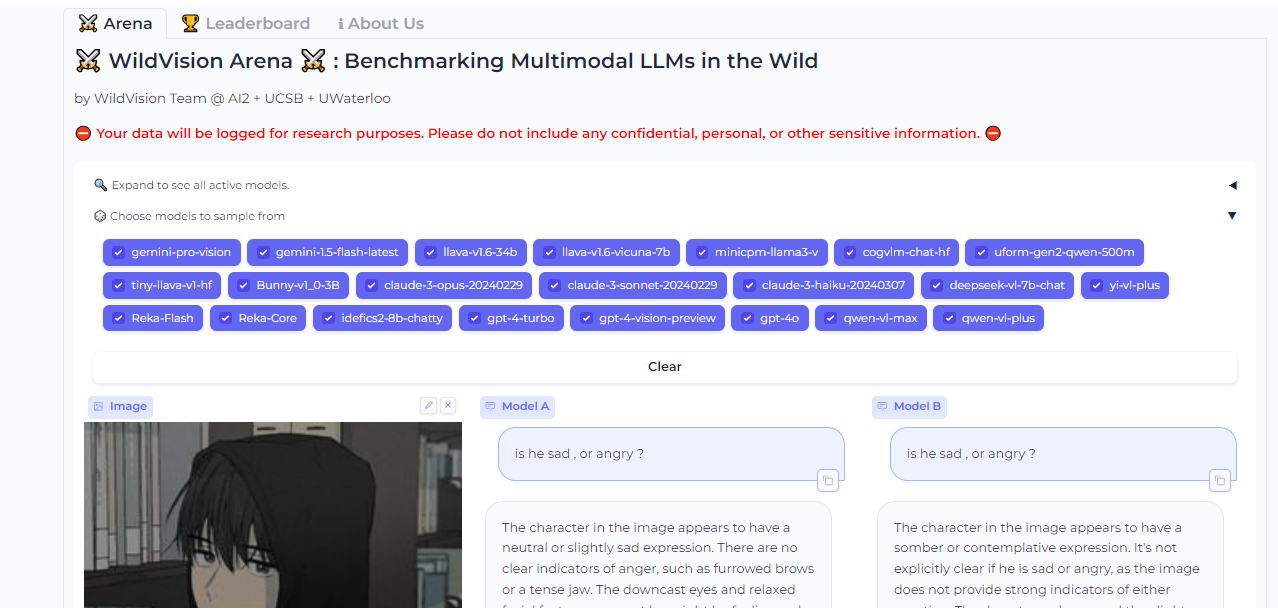
Vision Arena
Vision Arena is a leaderboard that ranks VLMs based on anonymous user voting and reviews. But what makes it great is the fact that you can compare any two models side-by-side for yourself to find the best fit for your application.
And when you compare two models, you can contribute your own anonymous votes and reviews for others to lean on as well.
OpenVLM Leaderboard
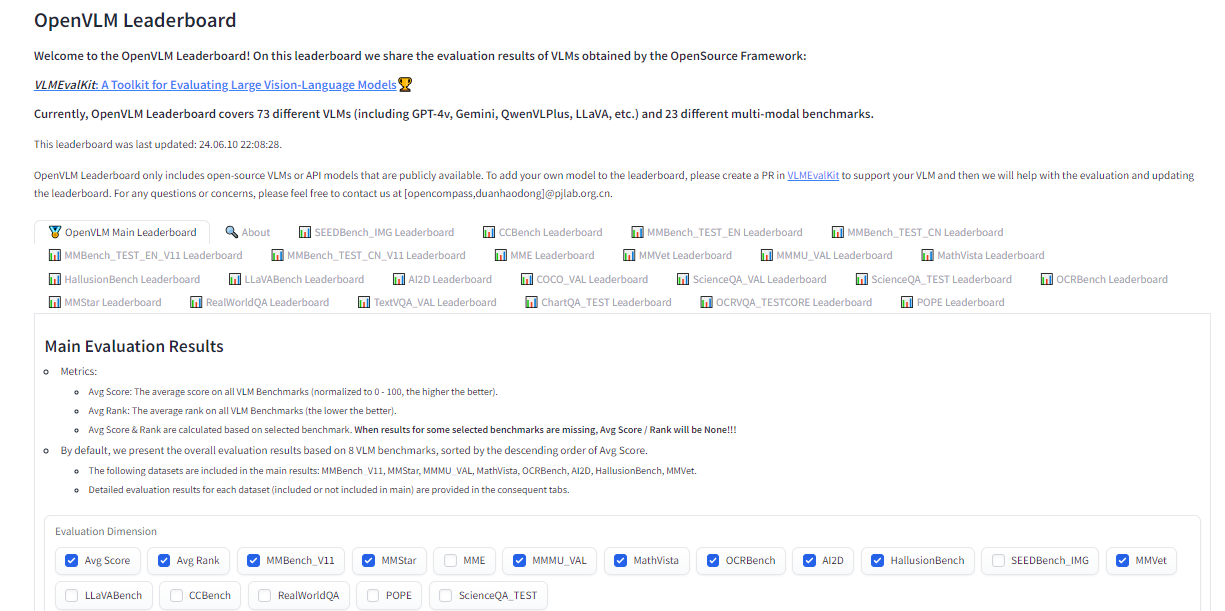
OpenVLM is another leaderboard hosted on Hugging Face for getting technical specs on different models. What I like about this resource is the wealth of metrics for evaluating VLMs, including the speed and accuracy of a given VLM.
Further, OpenVLM lets you filter models by size, type of license, and other ranking criteria. I find it particularly useful for finding VLMs I might have overlooked or new ones I haven’t seen yet.
Text-To-Speech Technology
Earlier, I mentioned that the app we are about to build will use vision-language models to generate written descriptions of images, which are then read aloud. The technology that handles converting text to audio speech is known as text-to-speech synthesis or simply text-to-speech (TTS).
TTS converts written text into synthesized speech that sounds natural. The goal is to take published content, like a blog post, and read it out loud in a realistic-sounding human voice.
So, how does TTS work? First, it breaks down text into the smallest units of sound, called phonemes, and this process allows the system to figure out proper word pronunciations. Next, AI enters the mix, including deep learning algorithms trained on hours of human speech data. This is how we get the app to mimic human speech patterns, tones, and rhythms — all the things that make for “natural” speech. The AI component is key as it elevates a voice from robotic to something with personality. Finally, the system combines the phoneme information with the AI-powered digital voice to render the fully expressive speech output.
The result is automatically generated speech that sounds fairly smooth and natural. Modern TTS systems are extremely advanced in that they can replicate different tones and voice inflections, work across languages, and understand context. This naturalness makes TTS ideal for humanizing interactions with technology, like having your device read text messages out loud to you, just like Apple’s Siri or Microsoft’s Cortana.
TTS Examples
Based on the use cases we covered alone, you can probably imagine that VLMs come in many forms, each with its unique strengths and applications. In this section, we will look at a few examples of VLMs that can be used for a variety of different purposes.
Just as we took a moment to review existing vision language models, let’s pause to consider some of the more popular TTS resources that are available.
Bark
Straight from Bark’s model card in Hugging Face:
“Bark is a transformer-based text-to-audio model created by Suno. Bark can generate highly realistic, multilingual speech as well as other audio — including music, background noise, and simple sound effects. The model can also produce nonverbal communication, like laughing, sighing, and crying. To support the research community, we are providing access to pre-trained model checkpoints ready for inference.”
The non-verbal communication cues are particularly interesting and a distinguishing feature of Bark. Check out the various things Bark can do to communicate emotion, pulled directly from the model’s GitHub repo:
[laughter][laughs][sighs][music][gasps][clears throat]
This could be cool or creepy, depending on how it’s used, but reflects the sophistication we’re working with. In addition to laughing and gasping, Bark is different in that it doesn’t work with phonemes like a typical TTS model:
“It is not a conventional TTS model but instead a fully generative text-to-audio model capable of deviating in unexpected ways from any given script. Different from previous approaches, the input text prompt is converted directly to audio without the intermediate use of phonemes. It can, therefore, generalize to arbitrary instructions beyond speech, such as music lyrics, sound effects, or other non-speech sounds.”
Coqui
Coqui/XTTS-v2 can clone voices in different languages. All it needs for training is a short six-second clip of audio. This means the model can be used to translate audio snippets from one language into another while maintaining the same voice.
At the time of writing, Coqui currently supports 16 languages, including English, Spanish, French, German, Italian, Portuguese, Polish, Turkish, Russian, Dutch, Czech, Arabic, Chinese, Japanese, Hungarian, and Korean.
Parler-TTS
Parler-TTS excels at generating high-quality, natural-sounding speech in the style of a given speaker. In other words, it replicates a person’s voice. This is where many folks might draw an ethical line because techniques like this can be used to essentially imitate a real person, even without their consent, in a process known as “deepfake” and the consequences can range from benign impersonations to full-on phishing attacks.
But that’s not really the aim of Parler-TTS. Rather, it’s good in contexts that require personalized and natural-sounding speech generation, such as voice assistants and possibly even accessibility tooling to aid visual impairments by announcing content.
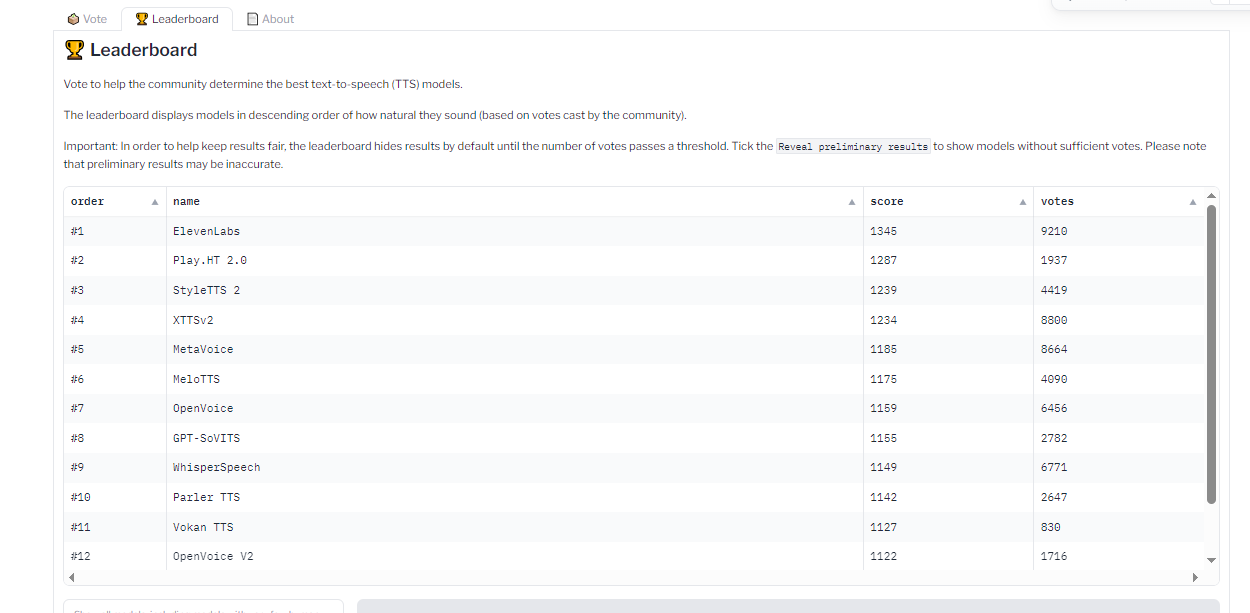
TTS Arena Leaderboard
Do you know how I shared the OpenVLM Leaderboard for finding and comparing vision language models? Well, there’s an equivalent leadership for TTS models as well over at the Hugging Face community called TTS Arena.
TTS models are ranked by the “naturalness” of their voices, with the most natural-sounding models ranked first. Developers like you and me vote and provide feedback that influences the rankings.
TTS API Providers
What we just looked at are TTS models that are baked into whatever app we’re making. However, some models are consumable via API, so it’s possible to get the benefits of a TTS model without the added bloat if a particular model is made available by an API provider.
Whether you decide to bundle TTS models in your app or integrate them via APIs is totally up to you. There is no right answer as far as saying one method is better than another — it’s more about the app’s requirements and whether the dependability of a baked-in model is worth the memory hit or vice-versa.
All that being said, I want to call out a handful of TTS API providers for you to keep in your back pocket.
ElevenLabs
ElevenLabs offers a TTS API that uses neural networks to make voices sound natural. Voices can be customized for different languages and accents, leading to realistic, engaging voices.
Try the model out for yourself on the ElevenLabs site. You can enter a block of text and choose from a wide variety of voices that read the submitted text aloud.
Colossyan
Colossyan’s text-to-speech API converts text into natural-sounding voice recordings in over 70 languages and accents. From there, the service allows you to match the audio to an avatar to produce something like a complete virtual presentation based on your voice — or someone else’s.
Once again, this is encroaching on deepfake territory, but it’s really interesting to think of Colossyan’s service as a virtual casting call for actors to perform off a script.
Murf.ai
Murf.ai is yet another TTS API designed to generate voiceovers based on real human voices. The service provides a slew of premade voices you can use to generate audio for anything from explainer videos and audiobooks to course lectures and entire podcast episodes.
Amazon Polly
Amazon has its own TTS API called Polly. You can customize the voices using lexicons and Speech Synthesis Markup (SSML) tags for establishing speaking styles with affordances for adjusting things like pitch, speed, and volume.
PlayHT
The PlayHT TTS API generates speech in 142 languages. Type what you want it to say, pick a voice, and download the output as an MP3 or WAV file.
Demo: Building An Image-to-Audio Interface
So far, we have discussed the two primary components for generating audio from text: vision-language models and text-to-speech models. We’ve covered what they are, where they fit into the process of generating real-sounding speech, and various examples of each model.
Now, it’s time to apply those concepts to the app we are building in this tutorial (and will improve in a second tutorial). We will use a VLM so the app can glean meaning and context from images, a TTS model to generate speech that mimics a human voice, and then integrate our work into a user interface for submitting images that will lead to generated speech output.
I have decided to base our work on a VLM by Salesforce called BLIP, a TTS model from Kakao Enterprise called VITS, and Gradio as a framework for the design interface. I’ve covered Gradio extensively in other articles, but the gist is that it is a Python library for building web interfaces — only it offers built-in tools for working with machine learning models that make Gradio ideal for a tutorial like this.
You can use completely different models if you like. The whole point is less about the intricacies of a particular model than it is to demonstrate how the pieces generally come together.
Oh, and one more detail worth noting: I am working with the code for all of this in Google Collab. I’m using it because it’s hosted and ideal for demonstrations like this. But you can certainly work in a more traditional IDE, like VS Code.
Installing Libraries
First, we need to install the necessary libraries:
#python
!pip install gradio pillow transformers scipy numpy
We can upgrade the transformers library to the latest version if we need to:
#python
!pip install --upgrade transformers
Not sure if you need to upgrade? Here’s how to check the current version:
#python
import transformers
print(transformers.__version__)
OK, now we are ready to import the libraries:
#python
import gradio as gr
from PIL import Image
from transformers import pipeline
import scipy.io.wavfile as wavfile
import numpy as np
These libraries will help us process images, use models on the Hugging Face hub, handle audio files, and build the UI.
Creating Pipelines
Since we will pull our models directly from Hugging Face’s model hub, we can tap into them using pipelines. This way, we’re working with an API for tasks that involve natural language processing and computer vision without carrying the load in the app itself.
We set up our pipeline like this:
#python
caption_image = pipeline("image-to-text", model="Salesforce/blip-image-captioning-large")
This establishes a pipeline for us to access BLIP for converting images into textual descriptions. Again, you could establish a pipeline for any other model in the Hugging Face hub.
We’ll need a pipeline connected to our TTS model as well:
#python
Narrator = pipeline("text-to-speech", model="kakao-enterprise/vits-ljs")
Now, we have a pipeline where we can pass our image text to be converted into natural-sounding speech.
Converting Text to Speech
What we need now is a function that handles the audio conversion. Your code will differ depending on the TTS model in use, but here is how I approached the conversion based on the VITS model:
#python
def generate_audio(text):
# Generate speech from the input text using the Narrator (VITS model)
Narrated_Text = Narrator(text)
# Extract the audio data and sampling rate
audio_data = np.array(Narrated_Text["audio"][0])
sampling_rate = Narrated_Text["sampling_rate"]
# Save the generated speech as a WAV file
wavfile.write("generated_audio.wav", rate=sampling_rate, data=audio_data)
# Return the filename of the saved audio file
return "generated_audio.wav"
That’s great, but we need to make sure there’s a bridge that connects the text that the app generates from an image to the speech conversion. We can write a function that uses BLIP to generate the text and then calls the generate_audio() function we just defined:
#python
def caption_my_image(pil_image):
# Use BLIP to generate a text description of the input image
semantics = caption_image(images=pil_image)[0]["generated_text"]
# Generate audio from the text description
return generate_audio(semantics)
Building The User Interface
Our app would be pretty useless if there was no way to interact with it. This is where Gradio comes in. We will use it to create a form that accepts an image file as an input and then outputs the generated text for display as well as the corresponding file containing the speech.
#python
main_tab = gr.Interface(
fn=caption_my_image,
inputs=[gr.Image(label="Select Image", type="pil")],
outputs=[gr.Audio(label="Generated Audio")],
title=" Image Audio Description App",
description="This application provides audio descriptions for images."
)
# Information tab
info_tab = gr.Markdown("""
# Image Audio Description App
### Purpose
This application is designed to assist visually impaired users by providing audio descriptions of images. It can also be used in various scenarios such as creating audio captions for educational materials, enhancing accessibility for digital content, and more.
### Limits
- The quality of the description depends on the image clarity and content.
- The application might not work well with images that have complex scenes or unclear subjects.
- Audio generation time may vary depending on the input image size and content.
### Note
- Ensure the uploaded image is clear and well-defined for the best results.
- This app is a prototype and may have limitations in real-world applications.
""")
# Combine both tabs into a single app
demo = gr.TabbedInterface(
[main_tab, info_tab],
tab_names=["Main", "Information"]
)
demo.launch()
The interface is quite plain and simple, but that’s OK since our work is purely for demonstration purposes. You can always add to this for your own needs. The important thing is that you now have a working application you can interact with.
At this point, you could run the app and try it in Google Collab. You also have the option to deploy your app, though you’ll need hosting for it. Hugging Face also has a feature called Spaces that you can use to deploy your work and run it without Google Collab. There’s even a guide you can use to set up your own Space.
Here’s the final app that you can try by uploading your own photo:
Coming Up…
We covered a lot of ground in this tutorial! In addition to learning about VLMs and TTS models at a high level, we looked at different examples of them and then covered how to find and compare models.
But the rubber really met the road when we started work on our app. Together, we made a useful tool that generates text from an image file and then sends that text to a TTS model to convert it into speech that is announced out loud and downloadable as either an MP3 or WAV file.
But we’re not done just yet! What if we could glean even more detailed information from images and our app not only describes the images but can also carry on a conversation about them?
Sounds exciting, right? This is exactly what we’ll do in the second part of this tutorial.




























